Linked list
In this article, we will see the introduction of linked list.
Linked list is a linear data structure that includes a series of connected nodes. Linked list can be defined as the nodes that are randomly stored in the memory. A node in the linked list contains two parts, i.e., first is the data part and second is the address part. The last node of the list contains a pointer to the null. After array, linked list is the second most used data structure. In a linked list, every link contains a connection to another link.
Representation of a Linked list
Linked list can be represented as the connection of nodes in which each node points to the next node of the list. The representation of the linked list is shown below -
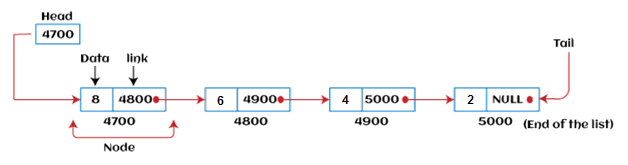
Till now, we have been using array data structure to organize the group of elements that are to be stored individually in the memory. However, Array has several advantages and disadvantages that must be known to decide the data structure that will be used throughout the program.
Now, the question arises why we should use linked list over array?
Why use linked list over array?
Linked list is a data structure that overcomes the limitations of arrays. Let's first see some of the limitations of arrays -
- The size of the array must be known in advance before using it in the program.
- Increasing the size of the array is a time taking process. It is almost impossible to expand the size of the array at run time.
- All the elements in the array need to be contiguously stored in the memory. Inserting an element in the array needs shifting of all its predecessors.
Linked list is useful because -
- It allocates the memory dynamically. All the nodes of the linked list are non-contiguously stored in the memory and linked together with the help of pointers.
- In linked list, size is no longer a problem since we do not need to define its size at the time of declaration. List grows as per the program's demand and limited to the available memory space.
How to declare a linked list?
It is simple to declare an array, as it is of single type, while the declaration of linked list is a bit more typical than array. Linked list contains two parts, and both are of different types, i.e., one is the simple variable, while another is the pointer variable. We can declare the linked list by using the user-defined data type structure.
The declaration of linked list is given as follows -
In the above declaration, we have defined a structure named as node that contains two variables, one is data that is of integer type, and another one is next that is a pointer which contains the address of next node.
Now, let's move towards the types of linked list.
Types of Linked list
Linked list is classified into the following types -
- Singly-linked list - Singly linked list can be defined as the collection of an ordered set of elements. A node in the singly linked list consists of two parts: data part and link part. Data part of the node stores actual information that is to be represented by the node, while the link part of the node stores the address of its immediate successor.
- Doubly linked list - Doubly linked list is a complex type of linked list in which a node contains a pointer to the previous as well as the next node in the sequence. Therefore, in a doubly-linked list, a node consists of three parts: node data, pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer), and pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
- Circular singly linked list - In a circular singly linked list, the last node of the list contains a pointer to the first node of the list. We can have circular singly linked list as well as circular doubly linked list.
- Circular doubly linked list - Circular doubly linked list is a more complex type of data structure in which a node contains pointers to its previous node as well as the next node. Circular doubly linked list doesn't contain NULL in any of the nodes. The last node of the list contains the address of the first node of the list. The first node of the list also contains the address of the last node in its previous pointer.
Now, let's see the benefits and limitations of using the Linked list.
Advantages of Linked list
The advantages of using the Linked list are given as follows -
- Dynamic data structure - The size of the linked list may vary according to the requirements. Linked list does not have a fixed size.
- Insertion and deletion - Unlike arrays, insertion, and deletion in linked list is easier. Array elements are stored in the consecutive location, whereas the elements in the linked list are stored at a random location. To insert or delete an element in an array, we have to shift the elements for creating the space. Whereas, in linked list, instead of shifting, we just have to update the address of the pointer of the node.
- Memory efficient - The size of a linked list can grow or shrink according to the requirements, so memory consumption in linked list is efficient.
- Implementation - We can implement both stacks and queues using linked list.
Disadvantages of Linked list
The limitations of using the Linked list are given as follows -
- Memory usage - In linked list, node occupies more memory than array. Each node of the linked list occupies two types of variables, i.e., one is a simple variable, and another one is the pointer variable.
- Traversal - Traversal is not easy in the linked list. If we have to access an element in the linked list, we cannot access it randomly, while in case of array we can randomly access it by index. For example, if we want to access the 3rd node, then we need to traverse all the nodes before it. So, the time required to access a particular node is large.
- Reverse traversing - Backtracking or reverse traversing is difficult in a linked list. In a doubly-linked list, it is easier but requires more memory to store the back pointer.
Applications of Linked list
The applications of the Linked list are given as follows -
- With the help of a linked list, the polynomials can be represented as well as we can perform the operations on the polynomial.
- A linked list can be used to represent the sparse matrix.
- The various operations like student's details, employee's details, or product details can be implemented using the linked list as the linked list uses the structure data type that can hold different data types.
- Using linked list, we can implement stack, queue, tree, and other various data structures.
- The graph is a collection of edges and vertices, and the graph can be represented as an adjacency matrix and adjacency list. If we want to represent the graph as an adjacency matrix, then it can be implemented as an array. If we want to represent the graph as an adjacency list, then it can be implemented as a linked list.
- A linked list can be used to implement dynamic memory allocation. The dynamic memory allocation is the memory allocation done at the run-time.
Operations performed on Linked list
The basic operations that are supported by a list are mentioned as follows -
- Insertion - This operation is performed to add an element into the list.
- Deletion - It is performed to delete an operation from the list.
- Display - It is performed to display the elements of the list.
- Search - It is performed to search an element from the list using the given key.
Complexity of Linked list
Now, let's see the time and space complexity of the linked list for the operations search, insert, and delete.
1. Time Complexity
| Operations | Average case time complexity | Worst-case time complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion | O(1) | O(1) |
| Deletion | O(1) | O(1) |
| Search | O(n) | O(n) |
Where 'n' is the number of nodes in the given tree.
2. Space Complexity
| Operations | Space complexity |
|---|---|
| Insertion | O(n) |
| Deletion | O(n) |
| Search | O(n) |
The space complexity of linked list is O(n).